What to Expect Before, During, and After Hysterectomy Surgery?
Table of Contents

Undergoing surgery can be an intimidating and overwhelming experience. However, understanding the procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes of the surgery beforehand provides you with a sense of control and familiarity. It enables you to make informed decisions, ask relevant questions, and mentally prepare for the procedure. This article will discuss all you need to know about hysterectomy and what to expect before, during, and after the surgery.
Hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves uterus removal (or the womb) due to reasons like abnormal bleeding, uterine prolapse, uterine fibroids, and cancer. Depending upon the disease for which the procedure is suggested, a hysterectomy may be partial or complete. Hysterectomy can also be of different types depending upon the tissues removed and the technique adopted.
Types of Hysterectomy
- Total Hysterectomy: This type of hysterectomy involves the removal of the uterus and cervix but spares the ovaries.
Another form of this technique is total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. It involves removing the uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes (salpingectomy), and ovaries (oophorectomy).
- Subtotal Hysterectomy: Also known as supracervical hysterectomy, this procedure involves the removal of the upper part of the uterus while preserving the cervix. Doctors usually advise this surgery to conserve hormonal and sexual function.
- Radical Hysterectomy: This technique involves the removal of the whole uterus along with some of the tissues, the cervix, and the top part of the vagina. Doctors generally advise this to prevent cancer from spreading to other parts of the body.
Another variation of this procedure, the radical hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy involves removing the uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and upper vaginal wall, along with some surrounding tissue and lymph nodes.
Preparing for Hysterectomy
Before the surgery, your doctor will review your medical history and ask whether you have had any previous surgeries or medical conditions. They will also conduct a physical examination to evaluate your current health status.
Your doctor may also ask you to get specific preoperative tests such as blood tests, urine tests, electrocardiogram (ECG), and imaging tests like MRI and ultrasonography. These tests will help your doctor have a better understanding of your condition and plan for the hysterectomy surgery.
Hysterectomy Procedure
The hysterectomy is carried out under anesthesia. It means you would be administered drugs that will render you unconscious during the surgery to prevent you from feeling any pain or discomfort. Typically, surgeons use general anesthesia for hysterectomies but can also use regional anesthesia (e.g., epidural or spinal anesthesia) in certain cases.
Before the surgery, your doctor will talk to you about the technique he will be using to perform the hysterectomy. Surgeons perform hysterectomies using various methods depending upon the site of incision and the tools used, such as:
- Abdominal hysterectomy: Abdominal hysterectomy is a technique where the surgeon makes an incision in the abdomen to access the uterus
- Vaginal hysterectomy: In a vaginal hysterectomy, the surgeon accesses the uterus through the vagina.
- Laparoscopic hysterectomy: In this technique, the surgeon makes a small incision in the abdomen and uses an instrument fitted with a camera to access and visualize the uterus.
- Robotic-assisted Hysterectomy: This is a minimally invasive hysterectomy technique similar to laparoscopic hysterectomy. However, the surgeon accesses the uterus using a robotic device.
Post-operative Care and Recovery:
After your surgery, you will be kept under close observation to monitor any unusual pain, discomfort, and other side effects. The duration of hospital stay may vary from a few hours to several days depending on the type of hysterectomy performed and your health condition.
Your doctor may prescribe you pain medications and antibiotics to help relieve post-surgery pain and prevent infections. They will also advise you to take ample rest and follow proper wound care instructions to facilitate a smooth recovery.
It’s important to avoid strenuous activities for a few weeks. You will also be required to have regular follow-up visits with your healthcare provider. During these visits, your doctor would monitor your healing progress and address any concerns you may have.
After a few days of rest, you can resume your usual activities gradually. You can go back to your job within a few weeks. However, if your job involves physical labor, you may need a longer recovery time before returning to work.
Risks and Complications
Short-term complications:
Like all surgeries, hysterectomy also carries a risk of side effects and complications. Common post-surgery short-term complications include infection at the incision site, excessive bleeding, and blood clot formation. Other complications may include damage to surrounding organs and anesthesia-related complications.
Long-term complications:
In the long term, hormonal changes may occur depending on the type of hysterectomy, leading to menopausal symptoms. The surgery can also weaken the pelvic muscles and ligaments, causing pelvic organ prolapse, urinary incontinence, and bowel movement issues. Some individuals may experience changes in their sexual urge and response following a hysterectomy.
Preventing complications:
While complications cannot be completely avoided, you can take certain measures to reduce the risk, such as following the pre-operative and post-operative instructions accurately, attending all scheduled follow-up appointments, and avoiding heavy lifting and strenuous surgeries post-surgery.
Alternatives to Hysterectomy
Your doctor may also suggest non-surgical treatment options as an alternative to a hysterectomy depending on the underlying cause. This may include medications, hormone therapy, pessary use, etc.
Various minimally invasive procedures are also available for treating conditions that previously required hysterectomy treatment. For example, uterine artery embolization (UAE) is one of the fibroids treatment options. Doctors may recommend endometrial ablation for hemorrhage. Healthcare providers also advise pessaries or prolapse support devices like FemiCushion in cases of uterine prolapse. These procedures aim to preserve the uterus and are desirable if you wish to get pregnant in the future.
It is also possible seek a second opinion from another healthcare provider to explore other treatment options according to your medical and personal needs.
Supervising Doctor of This Article

Koichi Nagao, MD PhD
Professor, Department of Urology, Toho University Faculty of Medicine
Director of Urinary tract reconstruction center, Toho University Omori Medical Center
Director of Reproduction Center, Toho University Omori Medical Center
Professor Nagao specializes in plastic surgery in the field of reproductive medicine. He completed eight years of plastic surgery training at Showa University before majoring in urology at Toho University. With his meticulous surgical techniques and careful examinations that combines urology and plastic surgery, Professor Nagao became a Board Certified Specialist with multiple associations including the Japanese Urological Association, the Japan Society for Reproductive Medicine, and the Japanese Society for Sexual Medicine.
The suggested Products
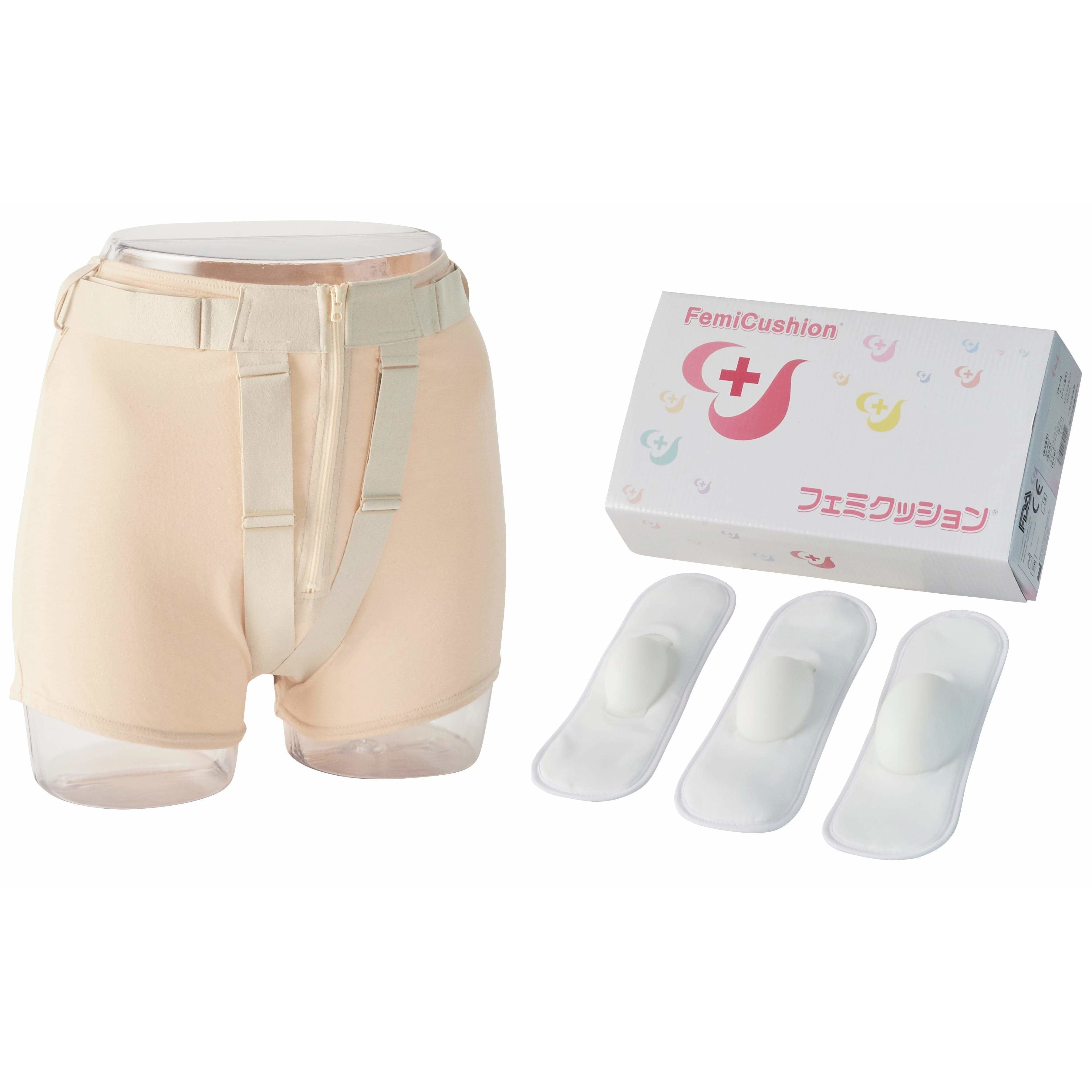

FemiCushion Lite Kit
$249.99
Kit FemiCushion EasyOpen Deluxe
$299.99
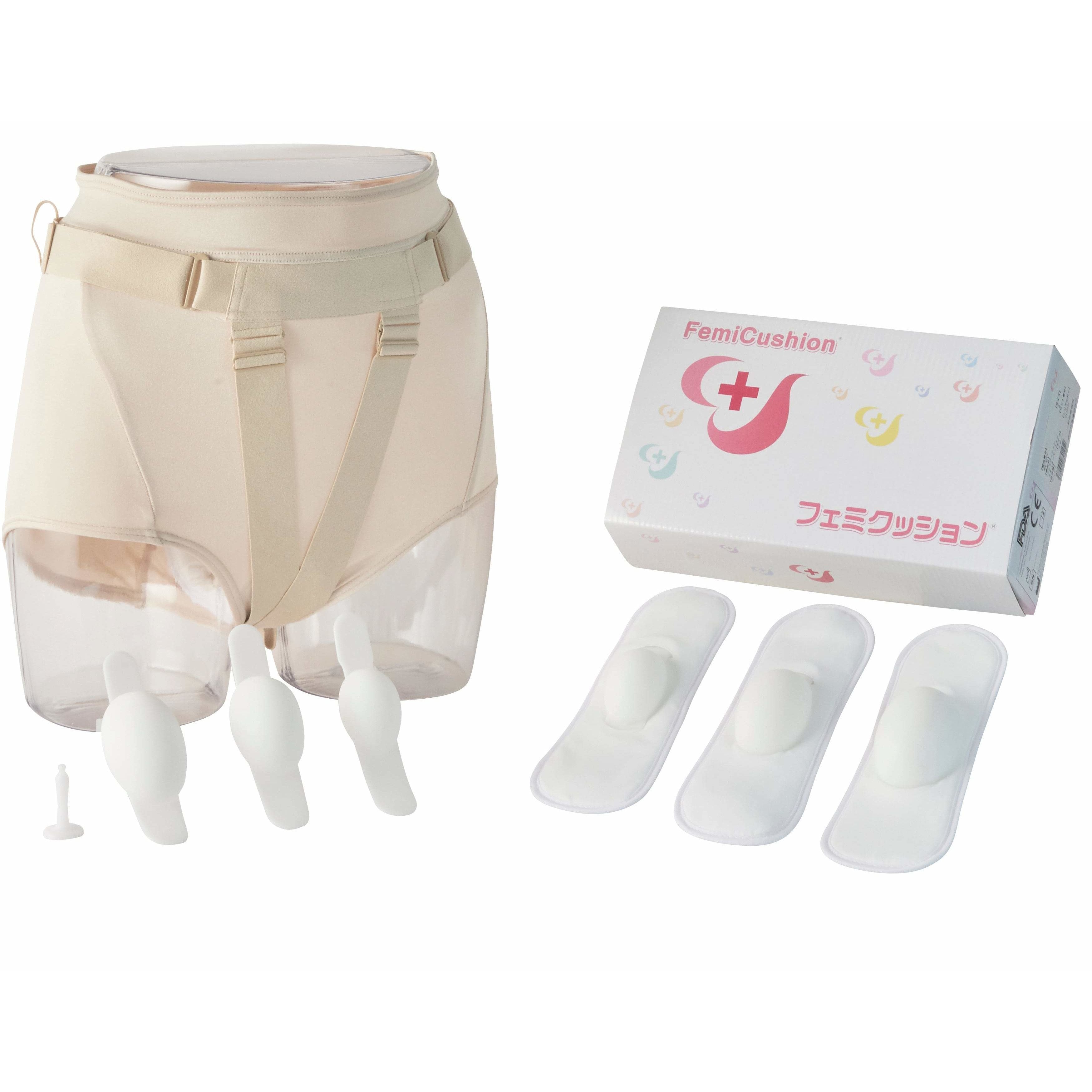

FemiCushion Standard Deluxe Kit
$299.99




